How To Find Sample Size Given Margin Of Error
Click here to jump to our Margin of Error Computer
When essential business organisation decisions are being made based on survey information from marketplace research, you lot need to know the data you're using is accurate and reliable.
Only can any market research — or any enquiry in general — be 100% accurate? How confident are you that your sample accurately reflects the population size as a whole?
While it's impossible for survey results to be completely representative all of the fourth dimension, you can figure out how close you are based on the margin of mistake built into your survey.
Merely what exactly is a margin of fault, how can y'all calculate information technology and how much can or should it bear on the level of confidence you have in your survey results?
Proceed reading to discover out.
What is margin of error?
Margin of fault is information that's provided alongside the results of a piece of research, such as a poll, survey, or a scientific study. Y'all'll recognize information technology considering it's expressed with a plus and minus sign together, e.g. + or -1%
Researchers use this to provide additional information that helps you interpret their results and to understand how the written report was carried out. The effigy tells you that the true result may differ from the percentage figure provided, and how much more than or less than the stated pct the reality might exist.
Margin of error provides a clearer understanding of what a survey'south estimate of a population characteristic means. A plus or minus ii percent points means that if we enquire this question using a simple random sample 100 times, 95 of those times it would come out at the estimated value plus or minus 2 points.
The larger your random sample (the more responses you get), the smaller your margin of error will be and the more confidence yous'll take that your sample results are reliable.
Notice out how big your sample size should exist with our gratuitous computer
When is margin of error used?
Margin of fault is used when you accept a random or probability sample.
That means the survey respondents have been selected at random from your population every bit a whole and every population member has a known, non-zero probability of being included.
It's not appropriate if the sample has been selected in a non-random way, for instance when you use an opt-in research panel.
A research panel sample is typically a quota sample, where participants are selected because they have particular characteristics. Additionally, the respondents volunteer for the panel in return for benefits, so they are not randomly selected from the population size at large.
And then although information technology is a popularly known term, it has a specific application in survey research and it won't e'er be relevant to your market research data.
Here are a couple of scenarios:
- A sports team has a complete list of anybody who has purchased tickets to their games in the past twelvemonth. If they randomly select a sample of that population for a survey, they can summate the margin of mistake on the percent of people who reported beingness a fan of the team.
- An organization has a complete list of employees. They poll a simple random sample of these employees on whether they preferred an additional twenty-four hour period of go out or a small bonus payment. They tin can study the margin of fault on the per centum preferring each option.
Other kinds of error
Margin of error accounts for the level of confidence you have in your results, and the amount of sampling fault you expect based on the size of the sample. But there are other kinds of survey errors that may influence your results likewise.
These include:
Coverage error
Where your sampling frame doesn't cover the population yous are interested in.
Non-response mistake
This happens when certain respondents don't have function in your survey.
Measurement fault
This can arise from problems with the questionnaire.
To learn about other sources of error, check out our guide to random and not-random sampling error.
What is a confidence interval?
A confidence interval (CI) is a range of values that include a population value within a caste of confidence.
The values are typically shown in the results as a % value when a population mean sits betwixt a lower and upper limit. Researchers use a CI to mensurate how accurately the survey sample resembles the overall population.
That'south because it's almost impossible to find a sample that 100% matches the characteristics of the total population.
Researchers can choose a CI of whatsoever level, only a 95% CI is the most common.
This ways researchers can exist 95% certain that the results contain the actual mean value of the total population. This tin can be demonstrated using a normal distribution:
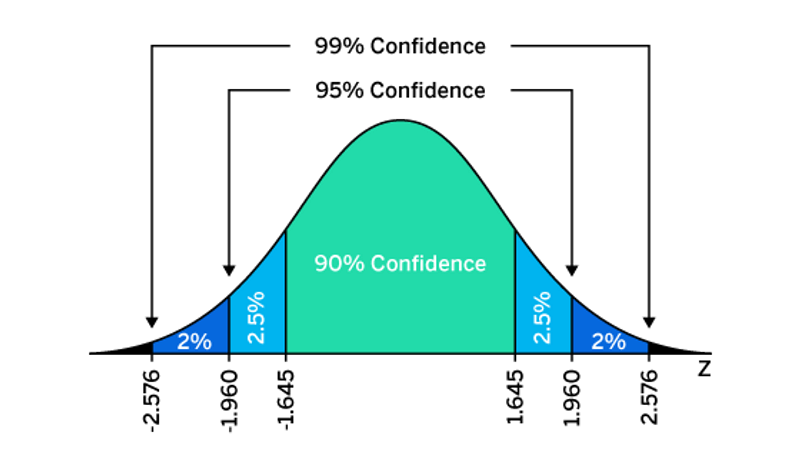
Using the graph above, you can see that if the probability of population mean value is between 1.96 and -i.96 standard deviations (sometimes called the z score), the sample hateful is 95% (hence the 95% CI).
This is the nigh common industry formula for calculating the CI. However, when the costs of an error are extremely loftier, e.chiliad. a multi-1000000 dollar decision is at stake, the confidence interval should be kept small. This can be done by increasing the sample size.
How do you calculate margin of error?
Margin of Fault Calculator
Margin of error is calculated using a formula:
Z * √((p * (1 – p)) / n)
Where
Z* is the Z*-value for your selected confidence level, which you'll look upwards in a table of Z scores:
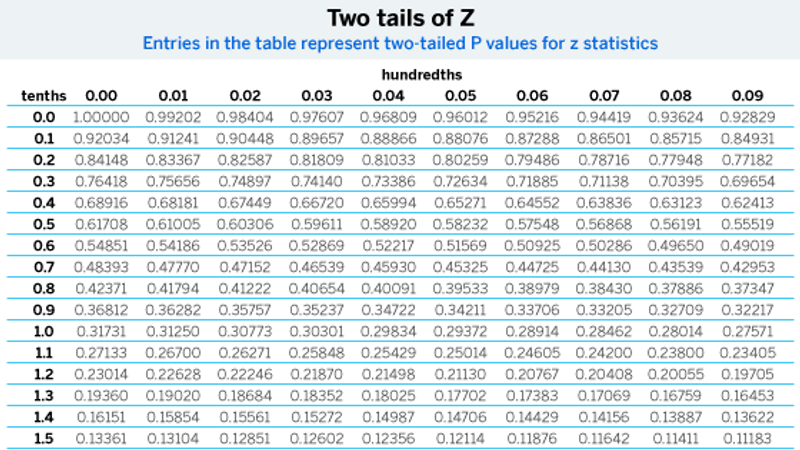
p is the sample proportion
n is the sample size
The sample proportion is the number within the sample that has the feature you're interested in. It'due south a decimal number representing a percentage, so while you're doing the calculation it's expressed in hundredths. For a five% sample proportion, information technology would exist 0.05.
The almost commonly used confidence level is 95%, so we'll apply that for an example calculation. The Z*-value for a 95% conviction level is 1.96.
We'll prepare our sample size at grand. Next, we'll follow the process to calculate the margin of error.
How to calculate margin of error with your survey data
- Subtract p from one. If p is 0.05, then one-p = 0.95.
- Multiply 1-p by p. So that'south 0.05 x 0.95 – which gives you 0.0475.
- Divide the result (0.0475) past the sample size n. And then 0.0475 divided past one thousand = 0.0000475.
- Now nosotros need the foursquare root of that value, which is 0.0068920. This is the standard error.
- Finally, nosotros multiply that number by the Z*-value for our CI, which is 1.96. And so 0.0068920 x ane.96 = 0.0134395. That'due south a margin of error of merely over 1%.
Let'southward try information technology with a real-world case.
Imagine you are a business organization surveying your current customers. You've run a study with a randomly selected sample of 1,000 people from your CRM list. The results tell you lot that of these 1,000 customers, 52% (520 people) are happy with their latest purchase, but 48% (480 people) are not – yikes. You lot desire to add a margin of error to these results when you report them to your shareholders.
Nosotros'll presume you want a 95% level of conviction, so the z*-value you're working with is once over again one.96.
The number of customers who are happy with their latest purchase was 520, so that'due south the number yous'll employ to piece of work out the sample proportion. 520 (p) / 1,000 (northward) = 0.52
- one-p is 0.48
- 0.52 (p) x 0.48 (1-p) = 0.2496
- 0.2496 / 1,000 = 0.0002496
- The square root of 0.0002496 = 0.0157987
- 0.0157987 x 1.96 (the z*-value) = 0.0309654, or in other words, 3.1% (when you round it up).
You can now report with 95% confidence that 52% of your customers were happy with their latest buy, + or – 3.1%
In that location are a couple of conditions for using this formula. They are:
- n x p must equal 10 or more than
- north x (1-p) must equal 10 or more
Normally, survey inquiry involves quite loftier numbers of people in a sample, so unless you have a very pocket-sized sample, or the sample proportion within your sample is very pocket-sized, there won't exist a trouble. If you're getting numbers beneath 10 for either of these checks, you may need to increment your sample size.
Free eBook:Learn how to increase response rates to your survey
Determining your sample size
Choosing the right sized sample is a critical part of creating a survey that will requite you reliable results, peculiarly when y'all're using the information to make critical business decisions.
Determining sample size is based on the number of people yous will need to stand for the full population. For example, using two,000 people every bit a representative sample of the UK workforce.
If you choose a sample that's too small, you won't get reliable results. The larger the sample, the smaller the margin of error. Of course, larger sample sizes mean costlier research, so ultimately at that place's a merchandise off.
Determining the size of your sample is a relatively straightforward process:
Calculate margin of fault
Your margin for error (also referred to as conviction interval) essentially determines how confident you lot tin can exist that your sample will represent the same results you lot'd become if you were able to survey the total population.
If you used the margin of fault formula mentioned above — Z * √((p * (i – p)) / n) — and the associated z score table, yous have your own margin of error calculator.
Understanding your confidence level
Your confidence level determines how certain you would exist that the bodily mean falls inside your margin of mistake — and that if y'all were to repeat your survey multiple times, yous'd still get the same results.
The lower your sample size, the lower your confidence level will be. The higher the sample size, the higher your confidence level.
What's the standard deviation likely to exist?
In a population, standard deviation helps you to empathise how the completed responses will differ from each other, every bit well as how they'll deviate from the mean number.
A depression standard difference means that the values are clustered effectually the mean number, whereas a high standard deviation means they are spread beyond a range, with some small and large outlying figures.
What's the total population size?
Population size is the main factor in determining the sample size you need to get the desired confidence level in your results.
The 'population' represents the whole group that you desire to empathize through your enquiry, while the sample size is the number of people you need to survey to get a representative sample of that whole.
Still unsure how to determine your sample size? Check out our Sample Size eBook.
How to reduce the margin of fault in your survey results
Reducing your margin of error is an essential part of increasing the reliability of your surveys and ensuring you're generating meliorate, more than accurate results.
There are several ways you can reduce the margin error, some are more practical and will depend on a few variables around your project.
Reduce the variables
Information technology stands to reason the more than variables yous have in your study the college the chances that errors will creep into your study.
Reducing the variables in the way you gather your sample or consummate your survey can also assistance to reduce the standard variation, meaning the margin of error will exist lower.
Increase the total number in your sample
Frequently the easiest way to reduce the margin for error is to increase the size of the sample. Having a larger group consummate your surveys statistically means you'll be more likely to generate a representative response for your report and reduce the margin of error.
Use a lower conviction level
A lower conviction level provides you with a more precise margin of mistake – nevertheless you should be wary about this as lowering the confidence level reduces the confidence that your survey volition accurately represent the overall population.
Use a unmarried-sided confidence interval
Unlike a two-sided CI, a single-sided interval has a smaller margin of fault, because information technology only shows if one of your parameters is higher up or beneath the cut-off value on i side i.e. information technology volition but tell y'all if the parameter is above or below (it won't show both).
You can employ this method to reduce your margin for error if you're confident the parameter will autumn on one side of the cut-off value.
How Qualtrics can help
No thing the survey, enquiry projection or poll, Qualtrics CoreXM has the tools and capabilities you lot need to derive insight from data — and get from insight to action.
Used by more than 13,000 customers, Qualtrics CoreXM brings your survey, inquiry, and polls into one platform, rather than multiple tools, enabling you to scale your activities, improve data quality, and uncover new opportunities.
With CoreXM, get insights faster through automation, reduce project costs and admin by consolidating your tools, and increase project impact by leveraging all-time-in-class survey methodologies and tools.
From uncomplicated polling and internal feedback surveys for strategy to gleaning customer, production, brand, and market place insights, Qualtrics CoreXM empowers every section to carry out and benefit from research.
And if you desire to get even more from your inquiry, accept advantage of Qualtrics' Research Services and a network of experienced partners. Through trainer experts, unlock cost and time savings, while benefiting from flexible service options that let you cull how much or how little support you need.
Desire to supercharge your inquiry? Find out more most Qualtrics CoreXM.
How To Find Sample Size Given Margin Of Error,
Source: https://www.qualtrics.com/experience-management/research/margin-of-error/
Posted by: campbellhavot1998.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How To Find Sample Size Given Margin Of Error"
Post a Comment